1. Skeletal Structure & Proportions
Pomeranians exhibit a distinct quadrupedal square build with a 1:1 body length-to-height ratio, though selective breeding has introduced subtle variations:Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
 Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
- Skull: Brachycephalic index of 85-90 (mesaticephalic range), with a 3:5 ratio of cranial vault to facial length
- Dentition: 42 teeth with notable frequency of oligodontia (14% lack premolars) and persistent deciduous teeth(22% cases)
Limb Geometry:Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
- Scapula inclination: 35° for optimized stride efficiency
- Femur-Tibia angle: 125° ±5°, predisposing to patellar issues
- Tail Vertebrae: 20-23 coccygeal bones forming the signature plume (vs. 18-20 in other Spitz breeds)
2. Coat ArchitectureArticle source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
Their iconic double coat undergoes four distinct growth phases:Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
- ①. Anagen Phase: 21-day active hair growth (guard hairs grow 0.6mm/day)
- ②. Catagen Phase: 7-day follicular regression
- ③. Telogen Phase: 30-day hair retention
- ④. Exogen Phase: Synchronized shedding during "coat blows"
Guard Hair Density: 400-600 hairs/cm² (compared to 200-300 in Chihuahuas)Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
Undercoat Characteristics:Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
- 18-22 µm fiber diameter
- Medullated structure with air pockets for insulation
- Color-Changing Mechanism: The TYRP1 gene mutation causes "puppy uglies" phase where 63% of Poms experience dramatic coat color shifts between 4-18 months
3. Pigmentation PatternsArticle source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
Recent studies identify six pigment distribution genes active in Pomeranians:Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
- ①. ASIP (Agouti): Controls sable/black patterns
- ②. MLPH (Melanophilin): Responsible for blue dilution
- ③. MITF (Microphthalmia): Linked to parti-color expression
- ④. TYRP1 (Brown locus): Modifies chocolate tones
- ⑤. KIT: Influences white spotting
- ⑥. CBD103: Determines dominant black
The rare merle pattern (present in 0.3% of Poms) results from SILV gene retrotransposon insertion, often accompanied by Waardenburg syndrome (15% incidence in merles).Article source:https://www.petwoah.com/Pet Site-https://www.petwoah.com/25.html
4. Sensory Specifications
Vision:
- 240° field of view (vs. human 180°)
- Dichromatic vision with peak sensitivity at 429 nm (blue) and 555 nm (yellow-green)
- Flicker fusion rate: 75 Hz (detects CRT TV scan lines)
Olfactory Capacity:
- 150 million olfactory receptors (1/3 of Bloodhounds)
- Can detect 1 ppb of amyl acetate in air
Auditory Range:
- 67 Hz to 45 kHz (human range: 20 Hz-20 kHz)
- Pinna mobility: 180° rotation in 0.3 seconds
5. Thermal Regulation System
Their compact size necessitates specialized thermoregulation:
Surface Area-to-Mass Ratio: 10.5 cm²/g (vs. 6.2 in Golden Retrievers)
Panting Efficiency:
300-400 breaths/minute during hyperthermia
Evaporates 0.25 mL water/minute per kg body weight
Brown Adipose Tissue: 5% of body mass (vs. 1% in humans), generating heat through uncoupled protein-1
6. Biomechanical Analysis
Gait studies using 3D motion capture reveal:
Trot Dynamics:
- Stride length: 0.8-1.2 times body length
- Peak vertical force: 120% body weight on forelimbs
Gallop Mechanics:
Suspension phase duration: 42% of stride cycle
Lead leg alternation every 3-5 strides for energy conservation
Jump Capacity:
Maximum vertical leap: 1.5 times shoulder height
Takeoff angle: 55° ±3° for optimal trajectory
7. Developmental Milestones
Dental Eruption Schedule:
- Deciduous: Incisors (3-4 weeks), Canines (5-6 weeks), Premolars (6 weeks)
- Permanent: Complete by 28 weeks except M3 (34 weeks)
Growth Plate Closure:
- Distal radius: 10-12 months
- Proximal tibia: 14-16 months
Coat Maturation:
Puppy coat replacement completes at 14-16 months
Guard hair terminal length achieved by 3 years
8. Extreme Phenotypes
Documented record-holders illustrate the breed's variability:
- Smallest: "Boo" (2.8 oz at birth, adult weight 1.1 lbs) with pituitary dwarfism
- Largest: "Bear" (12.3 lbs) carrying IGF1 gene mutation
- Longest Coat: "Jiffpom" (13" guard hairs) with FGF5 gene suppression
- Rarest Color: "Lilac" Pomeranian (1:50,000) from d/d + b/b genotype
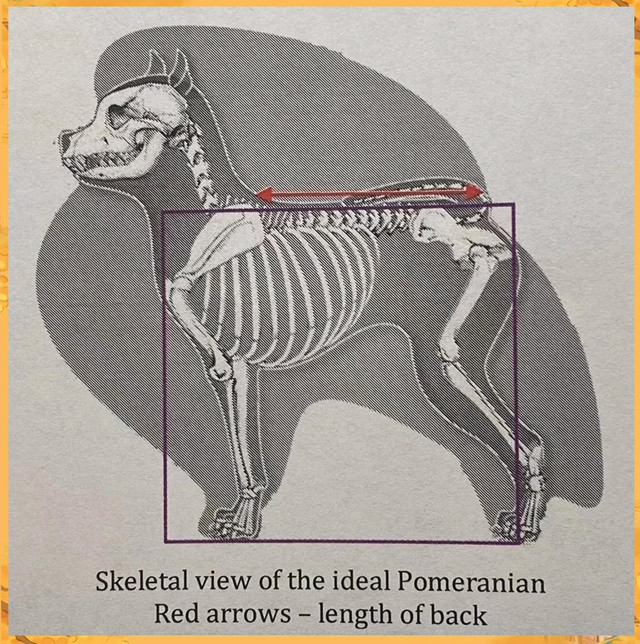
9. Comparative Anatomy
Key differences from ancestral German Spitz: